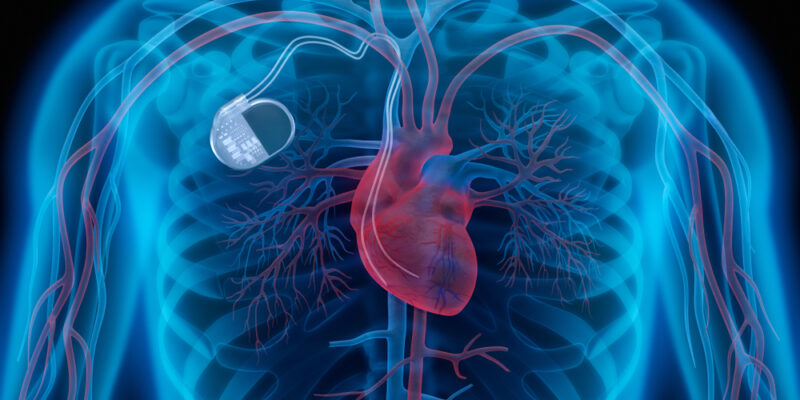
Irregular heartbeat, medically called “heart arrhythmia,” can be experienced by anyone at any given time. When this occurs, you may feel your heart beating in an irregular rhythm or it may also beat faster or slower than its usual rate. If you have been experiencing this often, it is best that you get a heart check up because it can either be harmless or life-threatening.
Symptoms of irregular heartbeat
Having a healthy heart does not guarantee that you will not ever experience irregular heartbeat as some heart arrhythmia may not give away any symptoms.
The most common signs that you can feel when having irregular heartbeat are:
- Anxiety
- Changes with vision
- Dizziness or light-headedness
- Fainting
- Feeling weak or extremely exhausted
- Pain or tightness in the chest
- Palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Strong pounding in the chest
- Sweating profusely
Causes of irregular heartbeat
A racing or fluttering heart can be caused by:
- A disease or injury affecting the heart
- Alcohol intake
- An infection
- Caffeine
- Certain medicines
- Drug abuse
- Genes
- Healing following a heart surgery
- Imbalance of electrolytes in the blood
- Exercise
- Fever
- Overwhelming emotions
- Sleep apnea
- Stress
- Tobacco use
When should you seek medical attention?
The heart is a very fragile and vital organ—anything that seems off or abnormal about its function warrants a physician’s attention. If you have been experiencing irregular heartbeat, whether it may be beating too fast, too slow, or skipping a beat, you can set an appointment to get a heart check up with a cardiologist in Singapore. A heart arrhythmia that is accompanied by symptoms, such as dizziness, fainting, fatigue, pain or tightness in the chest, or shortness of breath should be treated with urgency. Bring the patient to the closest hospital for treatment. Specifically, there are two types of irregular heartbeat that should seek medical attention immediately. These are:
- Bradycardia (slow heartbeat)
- Tachycardia (fast heartbeat)
Bradycardia occurs when the resting heart rate is beating less than 60 beats per minute. For some people who are fit physically, this may not be a problem. However, the condition can cause a concern when the heart rate is slow and the blood pumped by the heart is not enough to sustain the whole body. This kind of bradycardia can either be caused by:
- Conduction block
- Sick sinus syndrome
Tachycardia happens when the resting heart rate is over 100 beats a minute. This type of irregular heartbeat can be classified according to:
- Supraventricular arrhythmias – Atrial fibrillation (AFib), Atrial fluuter, Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT), Premature atrial contractions.
- Vetricular arrhythmias – Long QT syndrome, Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs), Ventricular fibrillation (V-fib), Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach).
Irregular heartbeat prevention
Practicing a healthy lifestyle can help prevent conditions or diseases that cause irregular heartbeat and affect the heart. You can do this by:
- Avoiding stressful situations
- Getting enough sleep and rest
- Eating a diet that is good for the heart
- Engaging in activities that can make your body healthy
- Keeping a healthy body weight
- Managing alcohol or caffeine intake to a minimum
- Maintaining medications prescribed by your doctor
Irregular heartbeat and Coronary Angiogram
One of the ways that can be done to diagnose heart arrhythmia is through a coronary angiogram.
A coronary angiogram is performed to check if there is any blockage that complicates the flow of blood through the heart. This heart test involves the use of X-ray to view the condition of the blood vessels of the heart.
The procedure is done in these steps:
- A dye is injected into the heart’s blood vessels. This kind of dye is observable with the use of an X-ray machine.
- The X-ray machine takes several images of the heart quickly and consecutively, showing the condition of the blood vessels.
- Any blocked arteries discovered during the test can be opened and treated by the doctor directly.
A coronary angiogram can determine the issues concerning the blood vessels in your heart, including:
- Checking the flow of blood through the vessels and heart
- Confirming the number of clogged coronary arteries
- Confirming the amount of blood that is unable to flow through the blood vessels due to blockage
- Determine the location of the clogging in the blood vessels
Due to some risks and complications, this test is usually done when necessary and after other non-invasive heart examinations have been utilised. Some cases require this heart test to be done during an emergency.
Preparing for a coronary angiogram
It is important that you follow your doctor’s instructions when preparing for a coronary angiogram. Generally, here are the preparations that you need to do before your scheduled procedure:
- Any food or drink consumption must not be done past midnight prior to your coronary angiogram schedule.
- Check with your doctor about medications that you need to take in the morning prior to your procedure.
- Make sure to bring all your medication bottles to the hospital on the day of your procedure.
- For patients diagnosed with diabetes, confirm with your doctor if there is a need for you to take insulin or other medications for diabetes before your coronary angiogram test.
Risks of coronary angiogram
The most common risk involved n a coronary angiogram procedure is the exposure to the X-ray’s radiation. There are other complications that can be major, but they rarely happen. These are:
- Adverse reactions to the dye used for the test
- Artery injuries
- Arrhythmias
- Bleeding excessively
- Damage to the kidney
- Heart attack
- Infection
- Stroke
It is important that you contact your doctor immediately or get emergency medical services if ever you experience any of these signs after your coronary angiogram procedure:
- A fresh bruise, inflammation, or bleeding in the treatment area
- Chest pains
- Colour or temperature change, numbness, or weakness in the arm or leg where the treatment area is located
- Fever or signs of infection at the site where the catheter was inserted
- Pain felt in the treatment area or where the catheter was inserted that worsens by the minute
- Shortness of breath
For more information about irregular heartbeat and coronary angiogram, reach out to Cadence Heart Centre.
Cadence Heart Centre
Mt. Elizabeth Hospital, 3 Mount Elizabeth #14-13
Mt Elizabeth Medical Centre, Singapore 228510
Mobile: (65) 8318 9884
Phone: (65) 6369 8789